Statistics I: Collection, Organization & Presentation of Data
Abdullah Al Mahmud
Data Collection
Types of Data
- Qualitative
- Quantitative
Sources of Data
Primary: Obtained directly (not collected from someone else)
- Secondary: Using pre-collected data from someone else/some organization
Example
- A researcher buys data from BMD to build a model of rainfall behavior
- A researcher runs an experiment to measure speed of light using a novel technique.
- A researcher makes use of the data generated by the one in example 2
Method of Data Collection
- Direct personal Inquiry
- Indirect oral inquiry
- Telephone etc.
- Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages;
Sources of Secondary Data
- Published: Journal, Newspaper etc.
- Unpublished: BBS, WHO, IMF, FAO, ICDDR,B
DIsadvantages of Secondary Data
- Purpose might be different
- Suitability
- Reliability
- Unit
Organizing Data
Tabluation

Data Classification
- Geographical
- Chronological
- Quantitative
- Qualitative
Example
Geographical
| Country | Bangladesh | USA |
|---|---|---|
| GDP(m) | 120 | 500 |
Chronological (Time series data)
| Year | 2015 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|
| GDP(m) | 120 | 500 |
Quantitative Classification
| Income level | 40,000-50,000 | 50,000-1,00,000 |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 120 | 34 |
Frequency Distribution
No. of classes
- Sturges Method: \(k = 1 + 3.322 \space logN\); where N = no. of observations
- Class Interval width = \({Range} \over {\text{Numbe rof classes}}\)
Graphs
Histogram
- Inclusive vs exclusive
What does it tell us
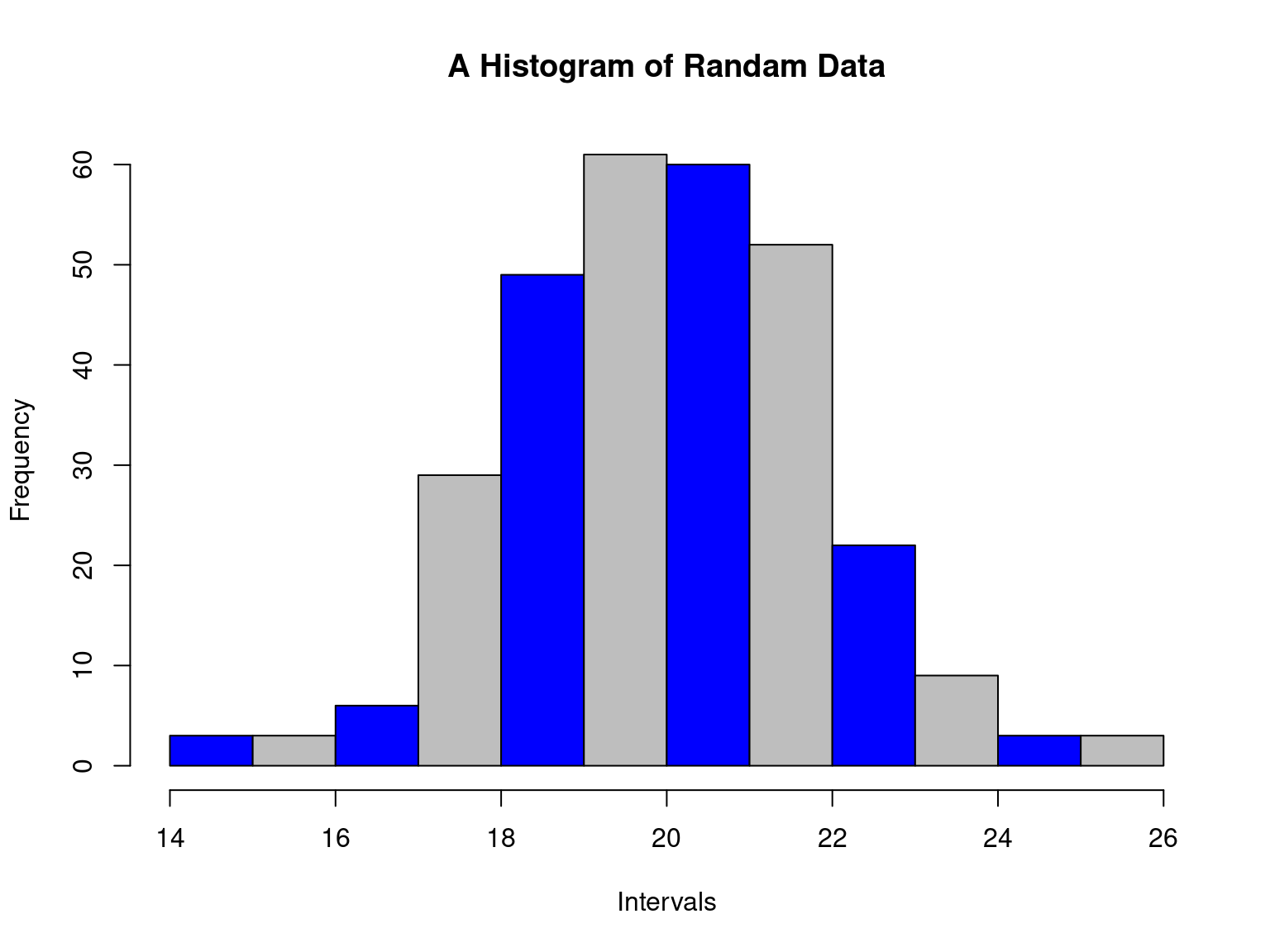
Histogram (contd.)
Can these intervals be readily used?
(5-10); (10-15); (15-20)
(5-9); (10-14); (15-20)
If not, what should we do?
Stem and Leaf
- key in stem and leaf plot
- How to interpret stem and leaf plot
##
## The decimal point is 1 digit(s) to the right of the |
##
## 0 | 1
## 1 | 0246
## 2 | 0567
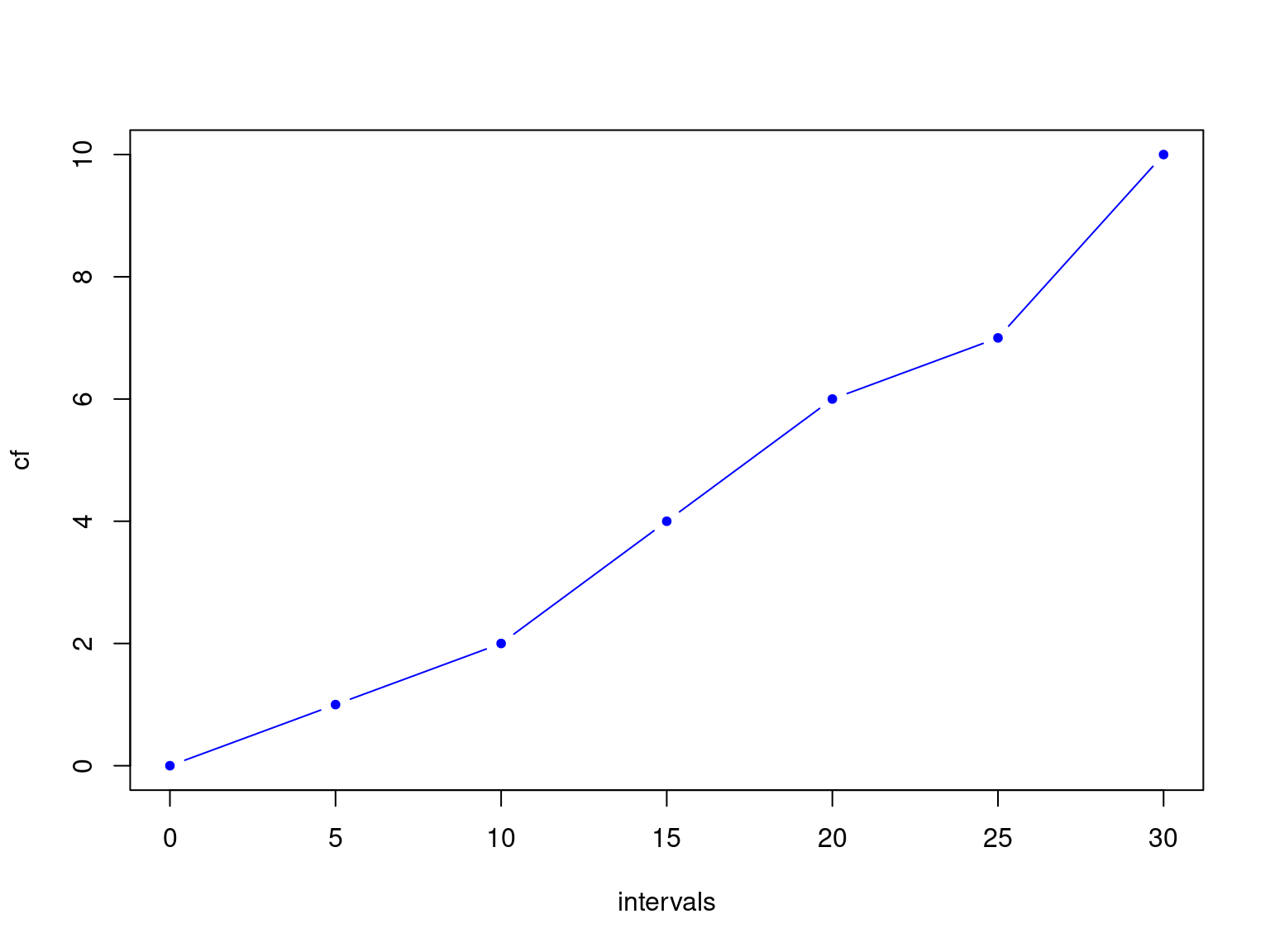
## 3 | 0How to interpret cf and rf
| Class | Frequency | Cumulative Frequency (cf) |
Relative Frequency (rf) |
Cumulative Relative Frequency (crf) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30-35 | 4 | 4 | 0.09 | 0.09 |
| 35-40 | 10 | 14 | 0.23 | 0.32 |
| 40-45 | 20 | 34 | 0.45 | 0.77 |
| 45-50 | 8 | 42 | 0.18 | 0.95 |
| 50-55 | 2 | 44 | 0.04 | 1 |
| n=44 | n=44 |
What Ogives tell us
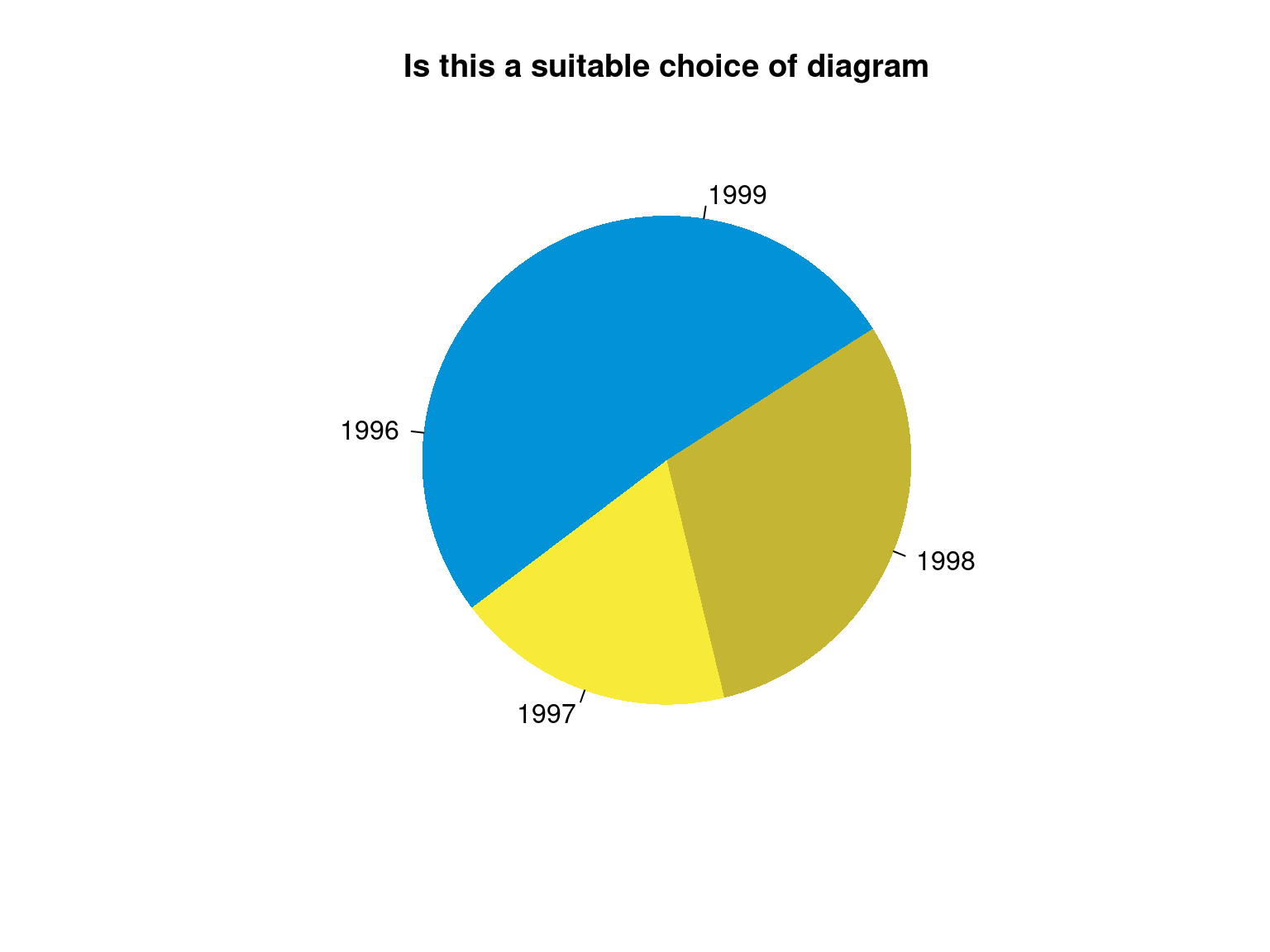
Bar vs Pie
- When to use which?
- How to calculate angles?
- Can we draw on 180 degrees?
Choose Diagram
| year | Sales ($) |
|---|---|
| 1996 | 76 |
| 1997 | 58 |
| 1998 | 95 |
| 1999 | 85 |
| Category | Cost(Tk.) |
|---|---|
| House rent | 10,000 |
| Utility Bill | 3,000 |
| Telecom | 2000 |
Frequency Polygon vs Frequency Curve
- Curve: Smoothed corners